The previous blog Part 1 included the definition,concept and history of cloud computing. Moving further we discuss on the different cloud service and deployment models.
Service Models:
Cloud Computing services can be offered through various service models , out of which the common ones are IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service) and SaaS (Software as a Service).
IaaS is a virtualized infrastructure wherein the virtual machines are configured together with virtualized data storage and network component. These are made available to the users to deploy and manage their own OS, middleware and applications. The cloud provider takes care of the Infrastructure management.
PaaS is a computing platform wherein the infrastructure is enhanced by the addition of preconfigured OS and middleware .Users can deploy and manage their own applications on the preconfigured software platform. The cloud provider manages the platform software.
SaaS is an application service where entire applications are provided on top of the managed software platform. Users are provided with ready to run applications which can be accessed via browser or client side web apps connected into an application web server operated by the provider. Here the provider manages the application service delivery to a defined user base.
Simply put,
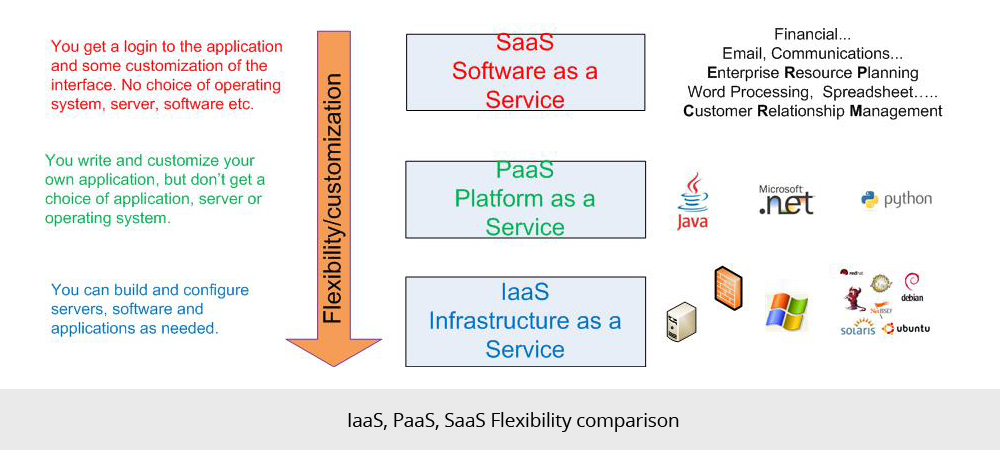
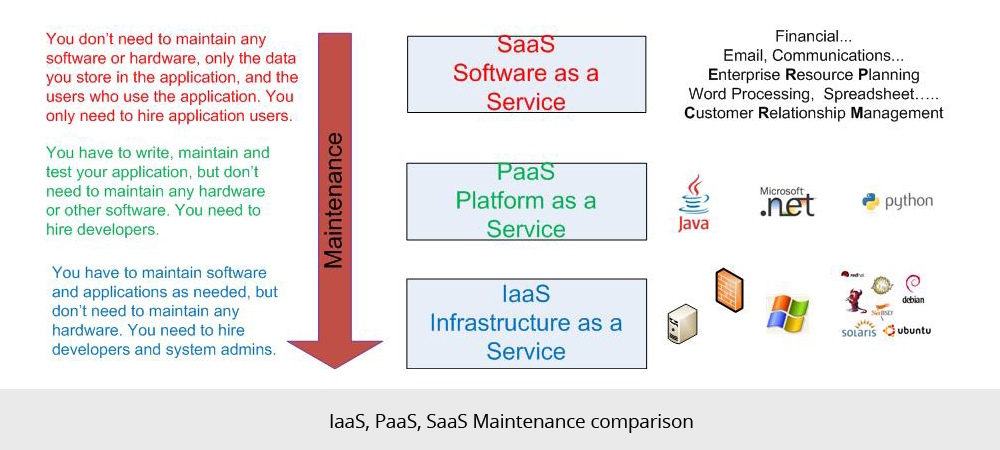
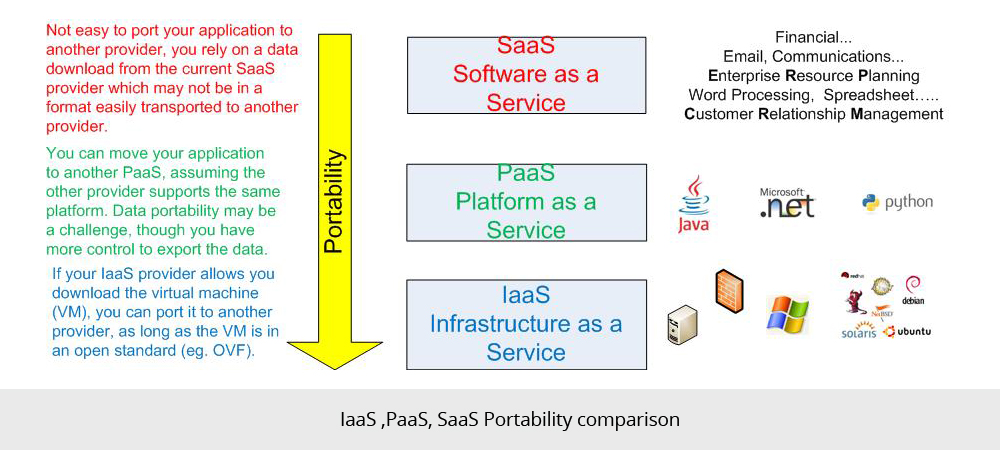
- If I use IaaS I get servers onto which I can load software and applications which I then maintain, though I don’t need to maintain the hardware. I can customize the applications and software running on the servers, at will.
- If I use PaaS, I get a platform of ready to use web servers, application servers, databases etc. I write my own software application and host it at the PaaS provider. I maintain the software I write, but not the application servers, databases or hardware. I can customize the software I write, at will.
- SaaS is a software that is rented rather than purchased. Instead of buying software and paying for periodic upgrades, SaaS is subscription based, and all upgrades are provided during the term of the subscription. When the subscription period expires, the software is no longer valid.
The images below show how IaaS, PaaS and SaaS differ with respect to respect to flexibility, maintenance and portability.
Flexibility:
Maintenance:
Portability:
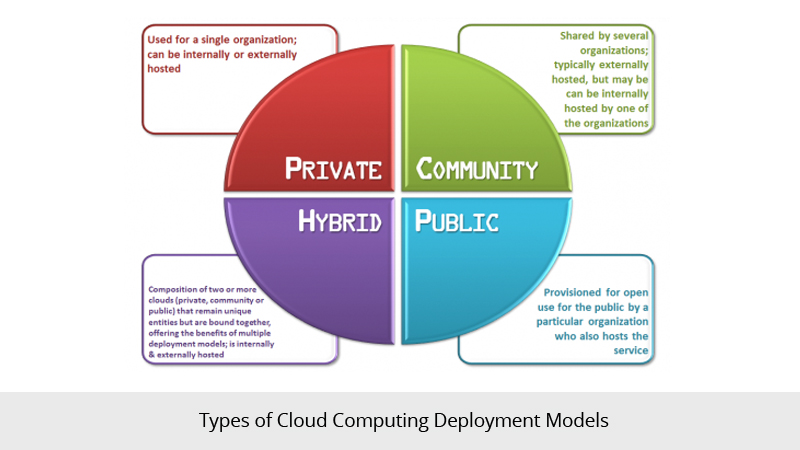
Deployment Models:
Private cloud: The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization comprising multiple consumers (e.g., business units). It may be owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises.
Community cloud: The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a specific community of consumers from organizations that have shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations). It may be owned, managed, and operated by one or more of the organizations in the community, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises.
Public cloud: The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for open use by the general public. It may be owned, managed, and operated by a business, academic, or government organization, or some combination of them. It exists on the premises of the cloud provider.
Hybrid cloud: The cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities, but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability (e.g., cloud bursting for load balancing between clouds).
For further reading refer, Cloud Computing- How much you know of it (Part-3) which includes the Pros, Cons and Conclusion.
References:
- National Institute Of Standards and Technology
- The Institution of Engineering and Technology
- Cloud Computing Journal